In an era defined by environmental urgency and stakeholder activism, the creeping menace of greenwashing threatens to undermine corporate sustainability reporting and erode stakeholder trust. As businesses face increasing regulatory and investor scrutiny, merely making sustainability claims is no longer enough; what matters is credible, independent ESG assurance and verification that convert words into trustworthy action. This article offers a critical opinion on why robust ESG assurance is essential—not only to protect corporate reputation but to ensure genuine commitment to ethical business practices. We will explore the current landscape of greenwashing, regulatory trends, assurance frameworks, and how effective ESG verification fosters authentic stakeholder trust.
Quick Takeaways (TL;DR)
- Greenwashing remains a critical risk as regulatory and stakeholder scrutiny intensifies in 2025.
- Robust ESG assurance and verification are essential to ensure accurate sustainability reporting and prevent reputational damage.
- Emerging global standards (IAASB, ISSB, CSRD) set frameworks for credible ESG assurance practices.
- Credible ESG assurance builds stakeholder trust among investors, consumers, and NGOs by validating corporate ESG claims.
- Legal and financial risks from greenwashing include lawsuits, fines, and market value erosion, which can be mitigated by assurance maturity.
- Implementing assurance requires overcoming data complexity, aligning governance, and leveraging technology for reliable ESG verification.
- The future favors corporations integrating verified ESG commitments into strategic decision-making for authentic, ethical business.
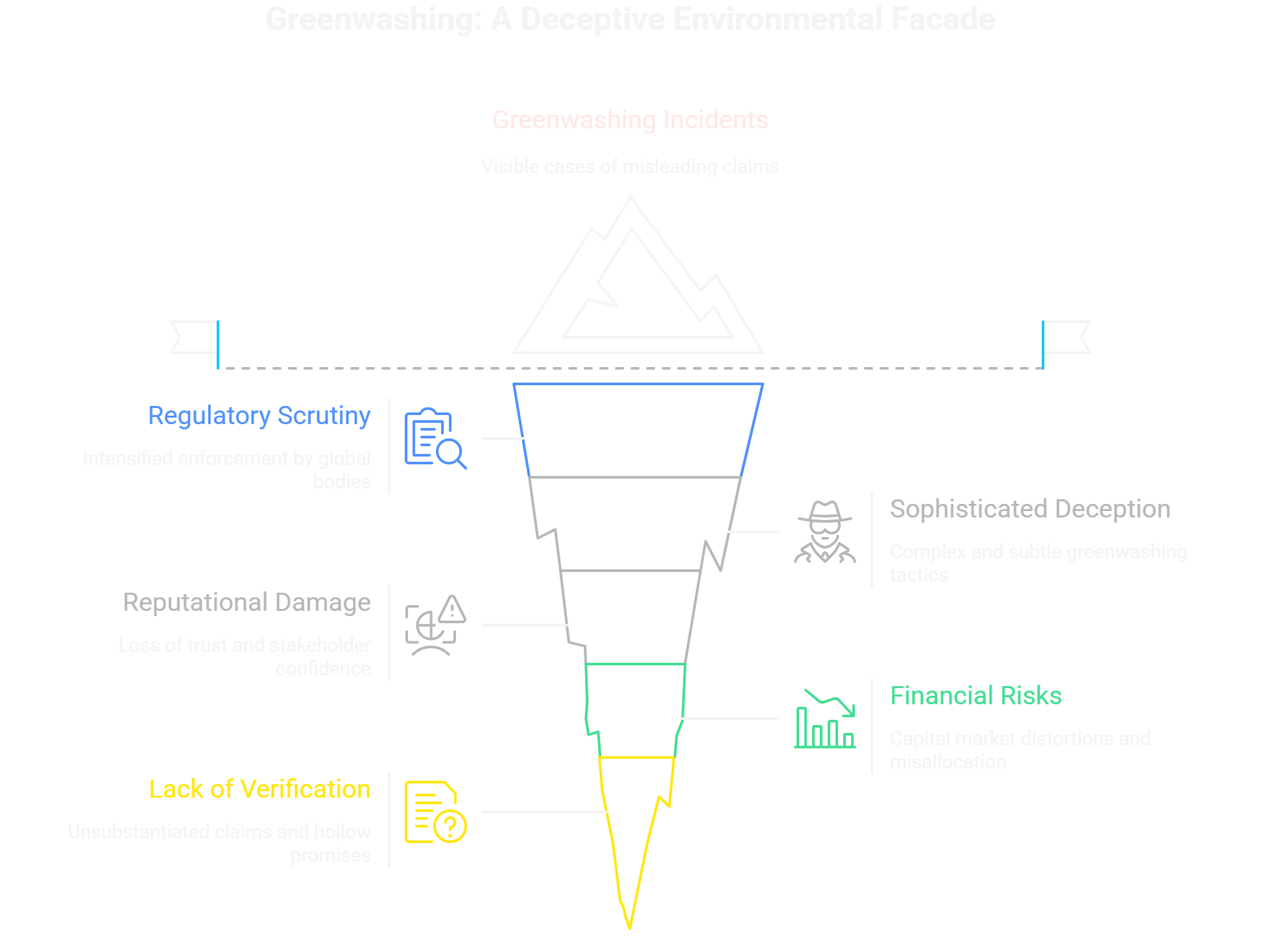
The Rising Threat of Greenwashing in 2025
Greenwashing refers to the misleading portrayal of a company’s environmental or social impact, often through exaggerated claims, vague language, or selective disclosures. In 2025, regulatory bodies worldwide—including the EU’s CSRD and Green Claims Directive—are intensifying efforts to clamp down on such practices by enforcing stringent verification and transparency requirements. While the overall number of companies flagged for greenwashing risk has declined, the severity of cases has notably increased, signaling the sophistication and complexity of deceptive claims. Recent high-profile incidents, such as financial institutions disengaging from sustainability alliances due to greenwashing exposure, demonstrate the reputational and legal perils of ignoring these warnings.
Greenwashing cases can manifest in false assertions about recycled content, unverified carbon footprint reductions, or hollow net-zero promises without corroboration. These varied tactics not only mislead stakeholders but also distort capital markets and slow down genuine progress toward environmental goals. For example, in retail—a sector highly visible to consumers—greenwashing scandals have triggered regulatory scrutiny and even board-level accountability for misleading ESG communication. Such developments underscore that greenwashing today is a multi-dimensional risk demanding urgent corporate response.
The Role of ESG Assurance in Combating Greenwashing
ESG assurance is an independent, external validation process that verifies the completeness, accuracy, and reliability of Environmental, Social, and Governance disclosures. Unlike internal audits or marketing claims, credible ESG assurance involves rigorous third-party examination against recognized standards, such as the International Auditing and Assurance Standards Board’s proposed ISSA 5000 and the EU CSRD’s assurance mandates. ESG verification confirms that sustainability data and claims withstand scrutiny and materially reflect company performance.
Emerging global standards are harmonizing ESG assurance methodologies, closing gaps that previously allowed greenwashing practices to thrive. Independent assurance benefits companies by enhancing stakeholder confidence, mitigating regulatory and litigation risks, and enabling more informed investment decisions. Moreover, it empowers sustainability leaders and PR teams to communicate authentic achievements, enhancing corporate reputation and fostering long-term stakeholder trust. Organizations that invest in robust ESG assurance signal a shift from performative sustainability to ethical business practices grounded in evidence.
How Robust ESG Assurance Enhances Sustainability Reporting
Robust ESG assurance significantly uplifts the quality of sustainability reporting by enforcing transparency, uniformity, and factual accuracy. Reports that undergo independent verification provide stakeholders with confidence that claims—such as emission reductions or biodiversity efforts—are not mere rhetoric but supported by reliable data and methodologies. This transparency translates into a stronger corporate reputation and builds resilience by preempting greenwashing accusations and regulatory penalties.
Many companies adopting assurance frameworks report higher investor engagement and better consumer perception due to increased credibility. For instance, companies subject to the EU CSRD’s external assurance requirements in 2025 saw improved integration of ESG data into financial disclosures, bridging gaps between sustainability and financial performance metrics. This integrated reporting aligns with emerging investor demands for holistic, trustworthy ESG information and reinforces the ethical foundations of corporate governance. The combination of detailed assurance and strategic communication is a unique lever seldom emphasized by competitors.
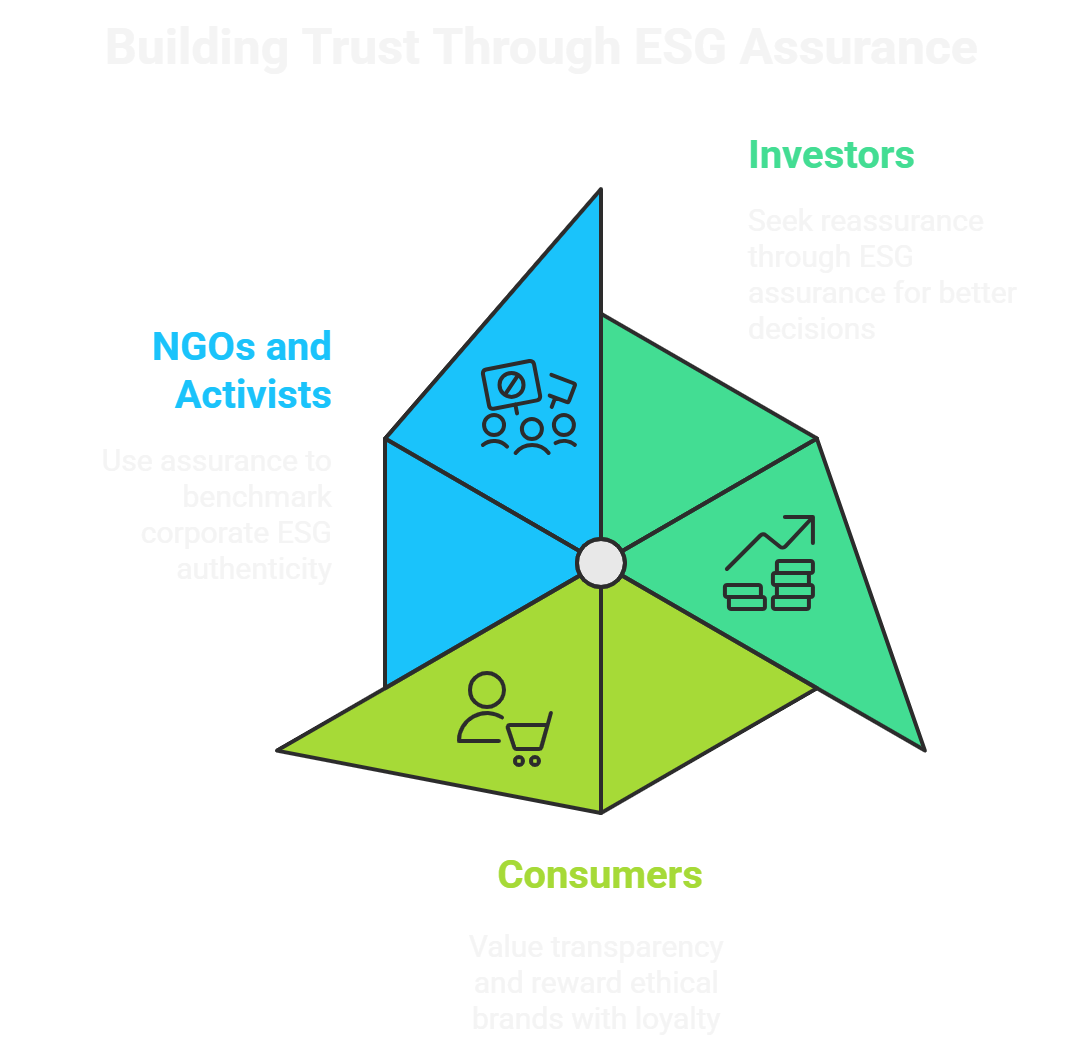
Stakeholder Trust: The Ultimate Outcome of Credible ESG Practices
Stakeholder trust—spanning investors, consumers, NGOs, and activists—is the ultimate benchmark of effective ESG practices. Research underscores a growing skepticism; surveys report that the vast majority of investors consider unsubstantiated sustainability claims a worsening problem. Consumers, especially younger demographics, increasingly scrutinize corporate ESG performance and reward transparent, verified conduct with loyalty and advocacy.
Strong ESG assurance reassures investors by reducing information asymmetry and enabling better fiduciary decisions, thereby attracting sustainable capital flows. At the same time, consumers rely on third-party verified claims to differentiate ethical brands and make value-aligned purchasing choices. NGOs and activist groups also use assurance as a barometer to benchmark corporate ESG authenticity and hold companies accountable. Thus, credible verification transforms verbal promises into tangible trust, forming the foundation of lasting corporate-stakeholder relationships.
Legal and Financial Implications of Greenwashing
Greenwashing exposes companies to escalating legal and financial consequences. The past five years have seen a doubling of ESG-related lawsuits worldwide, ranging from investor suits over fiduciary breaches to consumer and NGO litigations. Regulatory bodies such as the SEC, EU authorities, and the UK’s CMA are actively enforcing laws targeting misleading ESG claims, with clauses like the UK’s Green Claims Code imposing strict substantiation requirements.
Legal risks extend to fines, penalties, market value erosion, and increased scrutiny from regulators and shareholders. To mitigate these, corporations can leverage ESG litigation insurance products conditional on demonstrated ESG assurance maturity. Proactively embedding third-party verification into governance frameworks is an increasingly effective strategy to reduce greenwashing liabilities and protect financial interests, a unique angle often overlooked by companies still treating ESG disclosures as voluntary or secondary.
Implementing Effective ESG Assurance Programs: Challenges and Solutions
Although the value of ESG assurance is clear, companies face challenges including complex data gathering, inconsistent reporting frameworks, and board-level accountability gaps. Overcoming these hurdles requires aligning corporate governance structures with emerging ESG risks and reporting standards. Provision 29 of the UK Corporate Governance Code exemplifies how mandatory linkage between sustainability and risk reporting raises accountability.
Advanced technologies, such as digital ESG data platforms, AI analytics, and blockchain-enabled traceability, can enhance the verification process by improving data quality and audit trails. Sustainability leaders and PR teams must engage cross-functional teams, integrating ESG assurance into risk management and strategic decision-making. Addressing these operational challenges through a holistic approach is essential for companies aiming to build trust and resilience in an era intolerant of greenwashing.
The Future Outlook: Embedding Ethical Business through Verified ESG Commitments
Looking forward, embedding verified ESG assurance into core corporate strategy will differentiate ethical businesses from superficial sustainability performers. Global convergence of reporting and assurance standards—driven by ISSB, CSRD, and SEC rules—will create comparable, transparent sustainability metrics worldwide. This harmonization facilitates benchmarking and drives markets toward genuine ESG leadership.
Companies that embrace a culture of transparency, backed by rigorous ESG verification, will enjoy enhanced corporate reputation and stakeholder trust, fostering resilience against evolving regulatory and marketplace pressures. The era of unchecked greenwashing is ending; ethical business will be defined by verified commitments and a measurable positive impact. Corporate Boards and sustainability leadership should recognize assurance not as a compliance burden but as a critical enabler of enduring corporate value.
Conclusion
In today’s transparency-driven landscape, greenwashing poses more than a reputational inconvenience—it is a threat to market integrity and stakeholder relationships. As regulations tighten and stakeholder expectations rise, robust ESG assurance emerges as the cornerstone of authentic sustainability reporting and ethical business. Independent verification transforms sustainability claims from vulnerable assertions into credible commitments that build lasting stakeholder trust, protect corporate reputation, and insulate companies from legal and financial risks. Corporate Boards, Marketing & PR teams, Sustainability Leaders, Investors, and Consumers must therefore champion ESG assurance as a strategic imperative—not just a compliance checkbox. By prioritizing transparency and investing in reliable ESG verification today, businesses position themselves as trustworthy leaders capable of thriving in the evolving ESG ecosystem. To ensure your ESG claims are verifiable and credible, partner with independent assurance specialists who can help safeguard your reputation and foster genuine trust.
We’d love to hear your thoughts on the rising risks of greenwashing and the role of ESG assurance in building genuine trust. How is your organization navigating these challenges? Share your insights and experiences in the comments below, and if you found this article valuable, please share it with your professional networks to help promote ethical, transparent business practices.






